Construction Maintenance and Management Engineering LaboratoryLecturer Hiroyuki Ishimori
[2013/11/06]
If the waste we produce everyday is burnt, the ash will be released into the environment.
Similarly, when we create metal, slag is released into the environment, and when we make new buildings or roads, unneeded concrete will be released into the environment.
We can use this waste in an beneficial way as raw materials in engineering work. However putting this waste in landfills is not beneficial, not to mention that this waste contains chemicals harmful to the environment, and can cause land subsidence or destruction, poor drainage, and may change physical properties of the land, such as intensity, bearing power and water permeability.
We should recognize the characteristics of this system and consider how to deal with waste in order to mitigate risk in the future.
How can we control the environmental saftey of waste? Theory and practice.
Using the compression test or shearing test that we’ve all studied, strength can be tested and, using a permeability test, permeability can be tested.
The dissolution tests done by the Ministry of Environment, JIS, etc. can estimate the amount of hazardous chemicals that were absorbed by the material.
This kind of test is effective because the differences the characteristics for every material can be accounted for in the test conditions; the diameter of a sample particle, temperature, load, and time, can be adjusted to meet a specified level.
However, you must create a plan for a safe evaluation method for the environment.
This is because the intensity of chemicals and the amount of chemical released, are greatly influenced by how waste materials are used, for example, whether the waste material is granular or solid, anaerobic or aerobic, if fresh or salt water in present, rainfall, and temperature all have an effect.
Environmental safety evaluation in accordance with the conditions
You have to evaluate environmental safety according to the forms of use or conditions.
Fig.1 shows how the amount of elution will be different according to the form of the waste; (a) loosely covered, (b) packed in a flexible container, (c) solidified in concrete.
Based on standards set by JIS and other organizations, in order to assess the impact and what factors influence the amount of elution from waste, we can test the form and time by arranging the sample volume, adding a solvent, etc.
By understanding the factors affecting the amount of elution, we can recognize what we should be careful of at the waste site and how to deal with the waste.
Model experiment & numerical simulation
Generally this type of indoor trials finish within 24 hours, and at most in a few months.
However, at waste treatment plants and the sites where waste is used, the evaluation of environmental safety should start from now on to several decades.
So what should we do in this situation? We can use the technique called “model experiments & numerical values simulation”.
We are able to understand the mechanisms of the transportation or toxicity of chemical compounds elution of waste, and find out factors (similarity rule) and equations (dominant equation) which are dominant in the phenomena, and time and space scale-independent. By that, we estimate phenomena in real scale from results of model experiments or from calculation by substituting sizes or times of real scale.
Great East Japan Earthquake
When the Great East Japan Earthquake occured, waste from the disaster began after 1 week then after 1 month, the plan of temporary storage and landfill disposal was called for.
Because the waste was generated at the same time that radioactive material was released, a safety assessment of landfull disposal was crucial.
To plan the evaluation in the in the 1 month time limit, we could not test for a long time, or do large-scale testing, therefore, we collected knowledge by doing basic experiments which can be evaluated in 24 hours, then we determined the dynamic state of the radioactive material 100 years after using numerical value simulation, and planned the landfill disposal to match the required safety we needed.
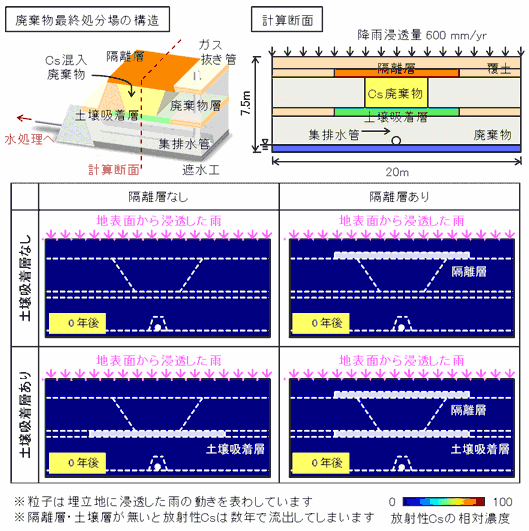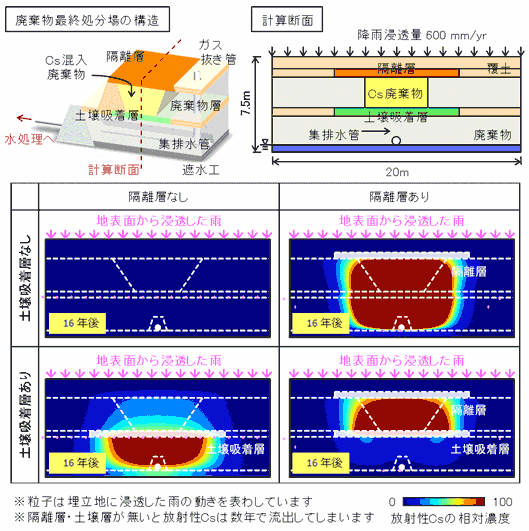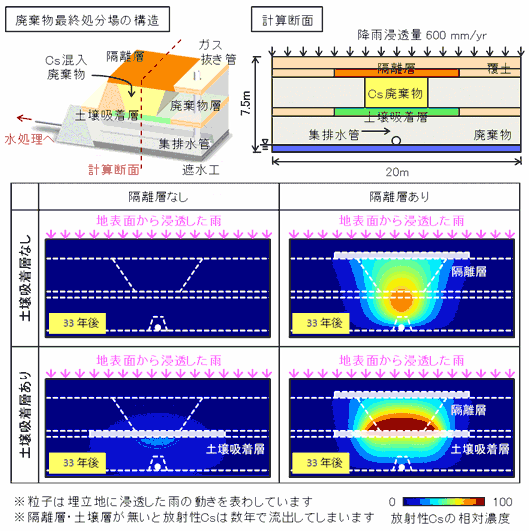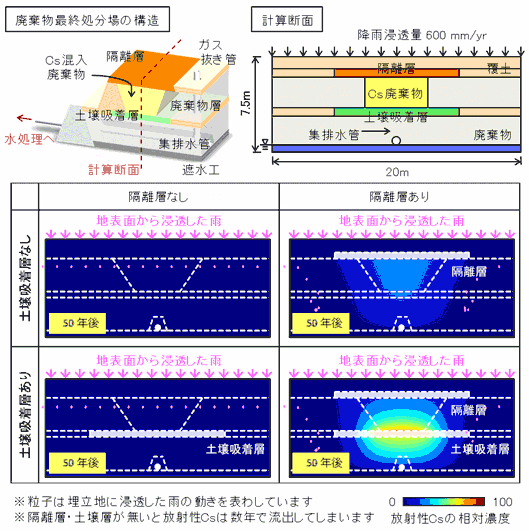
Fig. 2: Transport and distribution of radioactive cesium (Cs) when the Cs-contaminated waste is landfilled.
Fig.3 shows the concentration of radioactive Cs. when collector drain water flows into the water treatment facility.
To keep the radioactive material from spreading in the waste repository, it is effective to make an isolation layer on the top, and set the soil absorption layer under.
It necessary to be able to explain environmental safety in simple terms, so even those who are not specialists can understand.
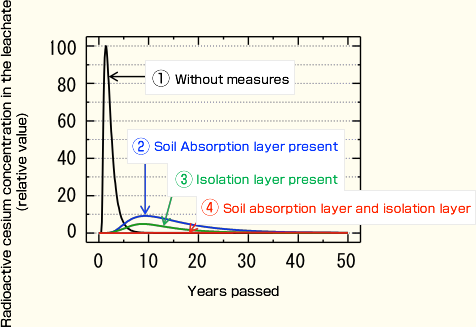
Fig. 3: Radioactive cesium concentration of leachate flowing into the water treatment facility
Professor’s profile
Construction Maintenance and Management Engineering Laboratory - Lecturer
Hiroyuki Ishimori|いしもり ひろゆき
In 1998, he began the Civil Engineering course of study at Ritsumeikan University.
After that, he entered the Environmental Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory and went on to the graduate school.
He undertook research for predicting material dynamics in the ground environment by mathematical analysis and model experiments.
For five years starting in 2009, he worked at the Resource Recycling and Waste Research Center in National Institute of Environmental Studies in the Ministry of the Environment.
There, he undertook research on waste processing and evaluation of environmental safety to promote safe and efficient use of burned ash and slag.
Also, he worked on research on practical measures and support for the government on interim storage and final disposal of radioactive pollutants which were generated after Great East Japan earthquake occurred.
I believe the Great East Japan earthquake should affect environmental education in Japan.
Japan is currently faced with the issue of how to use the lessons experiencing a big earthquake disaster, and ideas about reconstruction of the damaged area.
He thinks that environmental education needs not only to teach the history and difficulty of environmental pollution, but also to spare enough time to teach specialized knowledge and technology progress accumulated through science’s efforts to combat environmental pollution.
The public’s fear of toxic chemical compounds, especially radioactive materials, is tremendous. Therefore I strongly feel that researchers and educators should make an effort to educate young people, who can objectively understand the risks and consequences of our policies on environmental pollutants.
I would like to contribute to the education of today’s youth, even if only slightly, with my experience and memories from my involvement in environmental
administration and on-site work at the National Institute of Environmental Studies.
http://research-db.ritsumei.ac.jp/Profiles/56/0005550/profile.html




