
Susumu Nakata
Ritsumeikan University
Research topics
Shape modeling and solid mechanics
 Three-dimensional solid analysis of actual objects is performed
using the shape modeling technique in computer graphics
and the meshfree method.
The combination of the shape modeling and the meshfree analysis
enables computation without mesh structure of solids.
Three-dimensional solid analysis of actual objects is performed
using the shape modeling technique in computer graphics
and the meshfree method.
The combination of the shape modeling and the meshfree analysis
enables computation without mesh structure of solids.
Fast surface rendering using GPUs
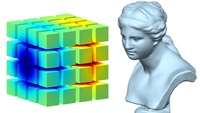 Direct rendering of smooth surfaces defined using implicit representation
are performed using GPUs.
The field defining a surface consists of a grid of polynomials
which contribute to efficient parallel computation on the GPUs.
Direct rendering of smooth surfaces defined using implicit representation
are performed using GPUs.
The field defining a surface consists of a grid of polynomials
which contribute to efficient parallel computation on the GPUs.
Acceleration of meshfree analysis using GPUs
 A parallel algorithm of the meshfree method for solving boundary value
problems is developed and implemented on a GPU.
The meshfree computation is effectively parallelized
by applying the idea of adaptive subdivison to the problem domain.
A parallel algorithm of the meshfree method for solving boundary value
problems is developed and implemented on a GPU.
The meshfree computation is effectively parallelized
by applying the idea of adaptive subdivison to the problem domain.
Inverse problems for identifying electrical inclusions
 A technique for the detection electrical inclusions in a body
using boundary measurement, called electrical impedance tomography,
is developed. Our approach enables detection of inclusions
using voltage-current measurements performed on a local area
of the boundary.
A technique for the detection electrical inclusions in a body
using boundary measurement, called electrical impedance tomography,
is developed. Our approach enables detection of inclusions
using voltage-current measurements performed on a local area
of the boundary.
Three-dimensional urban models based on historical GIS
 A scheme for creating large-scale urban three-dimensional models
based on historical GIS
data is developed. The models are generated as a set of automatically
located simple houses and indivisually produced buildings.
Our test shows that the historical city of Kyoto can be appropriately
reconstructed by the approach.
A scheme for creating large-scale urban three-dimensional models
based on historical GIS
data is developed. The models are generated as a set of automatically
located simple houses and indivisually produced buildings.
Our test shows that the historical city of Kyoto can be appropriately
reconstructed by the approach.