立命館大学 薬学部 細胞工学研究室のホームページ
Project
1.幹細胞分化とシグナル環境:シグナル環境が細胞分化に与える影響
今日我々の生活は、衣食住の全てにおいて様々な化学物質に取り囲まれており、これらと無縁に生活することは不可能と言って良い状態です。工業的に生産される化学物質は約10万種といわれ、プラスチック製品をはじめ医薬品、食品添加物、農薬などは我々の生活に多くの恩恵をもたらす反面、ヒトを含む地球上の生物に、ホルモン様活性を示し、内分泌かく乱作用を有することが明らかにされ、その悪影響が懸念されています。例えば魚介類にメス化等を引き起こす内分泌かく乱作用が有名です。一方でヒトに与える影響に関しては、男性不妊やアレルギー、乳がん、前立腺ガン、子供の神経発達、免疫能などへの影響が指摘されているものの、その影響を適切に評価するシステムが存在しないため、明確な結論が得られていません。
そこで当研究室では化学物質は、細胞分化過程のシグナル環境に影響する点に着目し、分化能を持つ幹細胞、ES, iPS細胞,生殖幹細胞を利用してその影響を解析しています。最近トランスクリプトーム、インフォマティクス解析によりプラスチック原料のビスフェノールAが生殖機能全般、そしてレチノイン酸シグナルに影響することを見出しました。現在、ヒトiPS細胞、ゼブラフィッシュ胚を用いた遺伝子発現解析により、そのメカニズムの解明に取り組んでいます。手法としては、遺伝子発現の量的変化に加え、whole mount in situ hybridizationなどを用いた時間的、空間的な遺伝子発現解析も使用しています。
また、肥満に関与する脂肪酸受容体のKO、TGマウスを用いたiPS細胞の作製、それらの脂肪細胞への分化実験による肥満予防・治療研究も行なっています。
Human iPS Cells
Zebrafish Embryo
Whole mount In-situ hybridization
関連論文
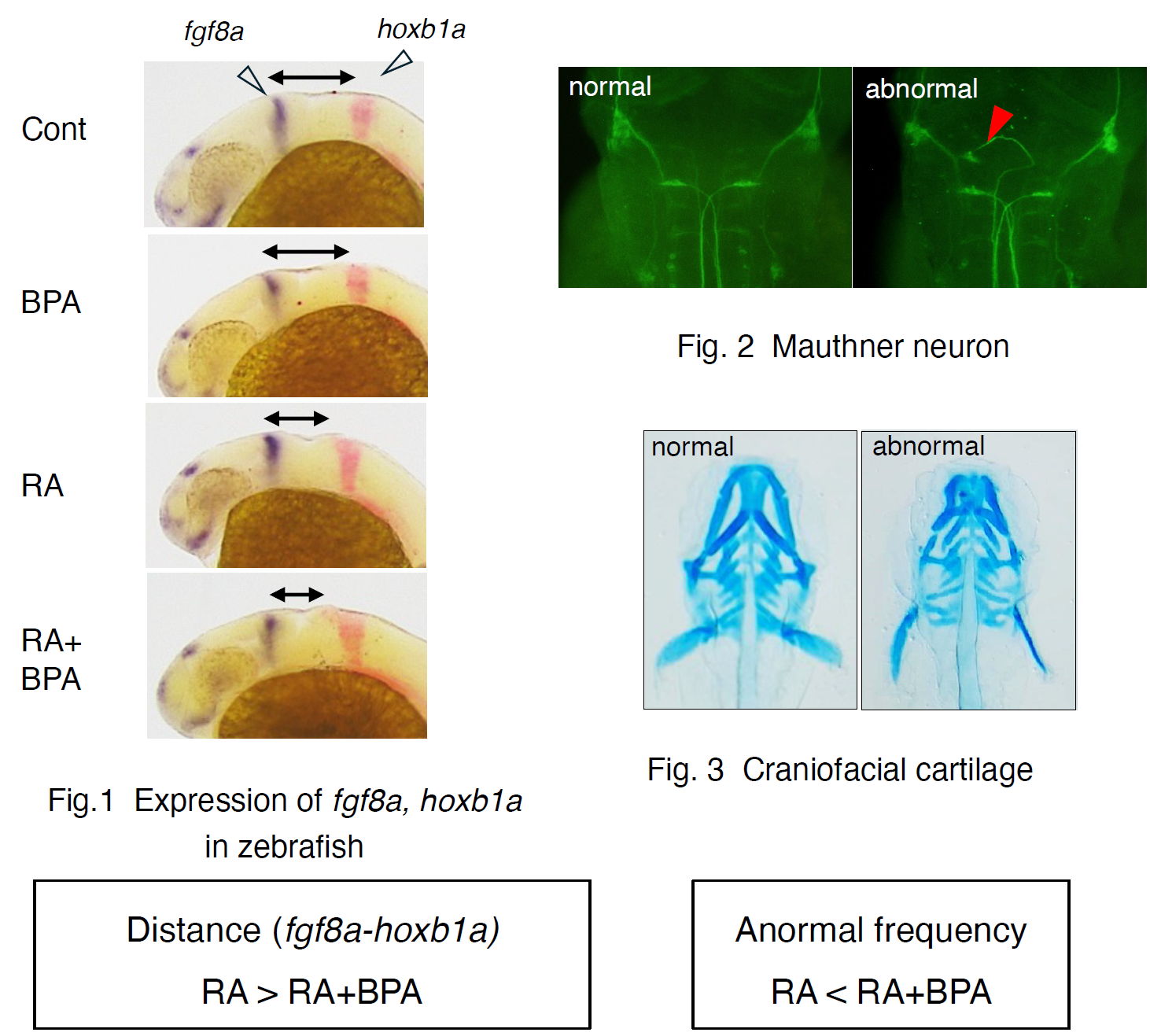
Effects of Bisphenol A and Retinoic Acid Exposure on Neuron and Brain Formation: a Study in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Zebrafish Embryos
Plastic pollution and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are emerging environmental concerns with potential impacts on human health and development. However, the underlying causal mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we show quantitative evidence that chemical exposure and detrimental outcomes are mechanistically linked to interference with retinoic acid (RA) signaling. Utilizing human induced pluripotent stem cells and zebrafish embryos, we found that BPA potentiated exogenous RA effects on 3′HOX gene expression and brain patterning, resulting in abnormalities such as duplication of Mauthner cell and abnormal craniofacial cartilage defects. RA receptor but not estrogen receptor is responsible for this signaling. Our findings provide a causal link between chemical exposure and neurodevelopmental impairments, contributing to the potential adverse effects of plastic pollution on development processes.
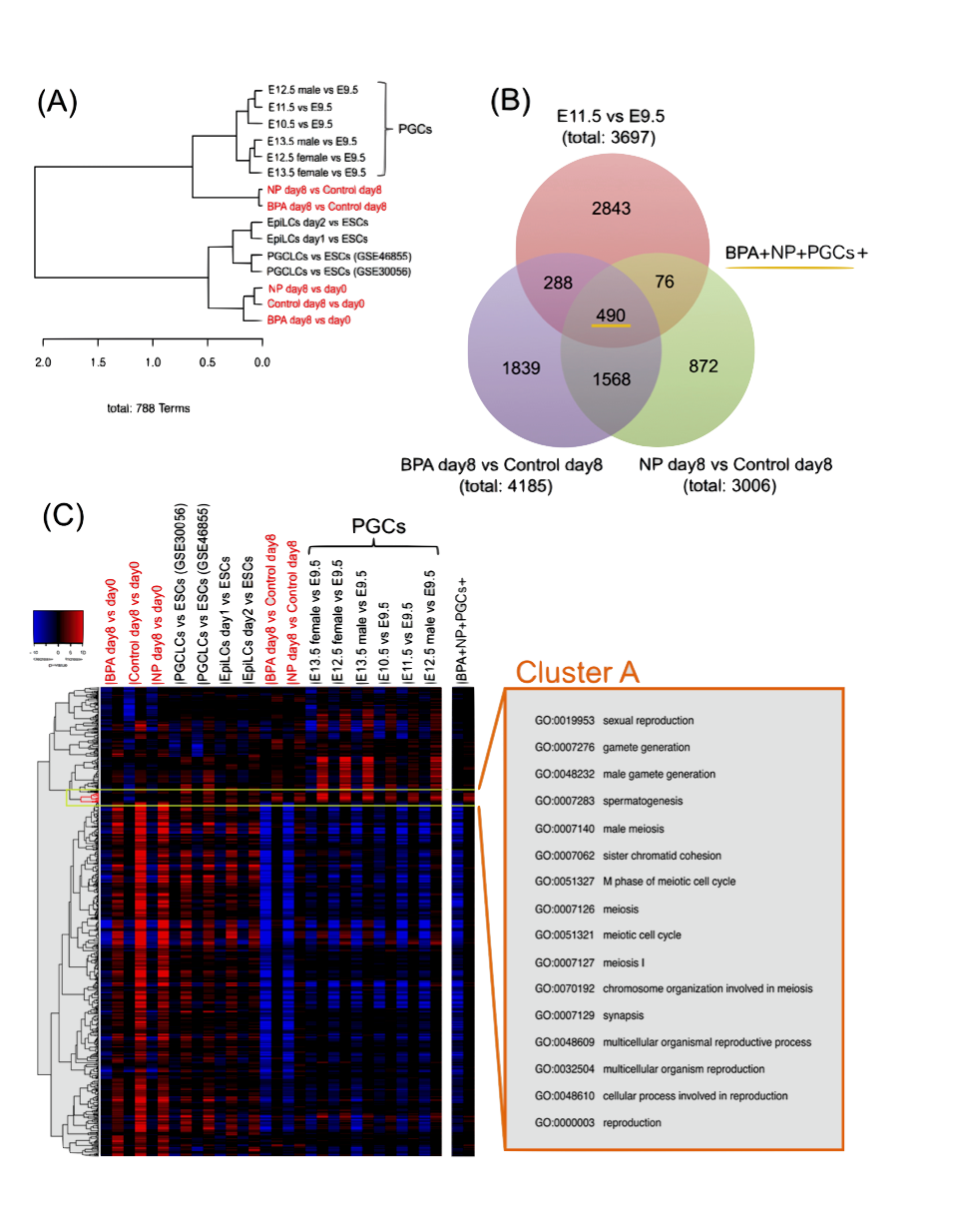
Transcriptome analysis revealed bisphenol A and nonylphenol affect reproduction
We investigated the effect of Bisphenol A (BPA) and Nonylphenol (NP) on cell differentiation, comparing transcriptome of EDC treated ES cells to that of normal germ cell development deposited in GEO data base. GO-based gene set enrichment analysis revealed that EDCs functionally affect wide range of reproduction by the modification of gene expression of germ cell specific genes especially related to meiosis.
Reproductive Toxicology 2019DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2019.06.006
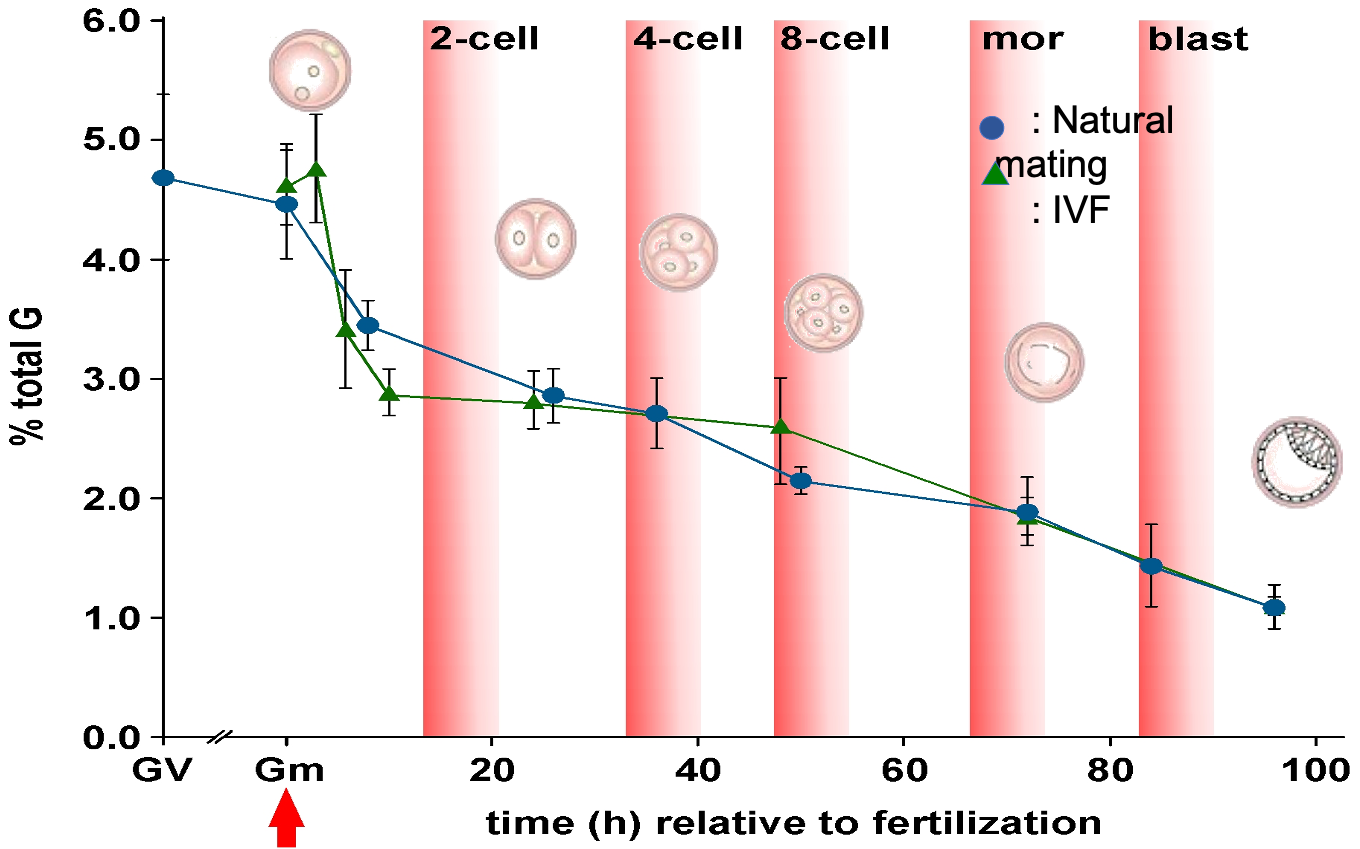
DNA methylation dynamics in mouse preimplantation embryos revealed by mass spectrometry
We here report direct quantification of genomic 5-methyl-2′-deoxycytidine (5 mC) and 5-hydroxymethyl-2′-deoxycytidine (5 hmC) and their dynamics of mouse embryos during preimplantation development using small scale liquid chromatographic tandem mass spectrometry (SMM)
Scientific Reports 2016DOI: 10.1038/srep19134
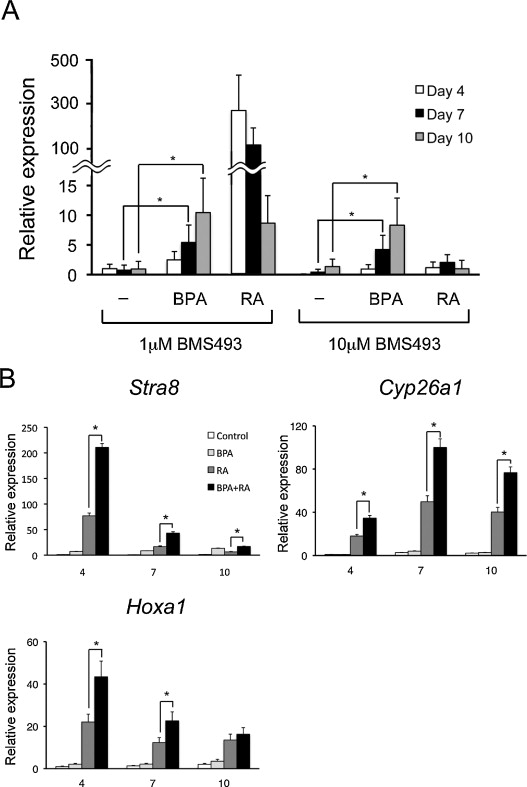
Bisphenol A modulates germ cell differentiation and retinoic acid signaling in mouse ES cells
In this study we investigated the effect of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDC) on cell differentiation using embryonic stem (ES) cells. We reported that BPA affect the expression of germ cell marker genes and retinoic acid signaling during in vitro differentiation of ES cells.
Reprod. Toxicol. 2012
DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2012.
06.001
