NEWS
[PRESS RELEASE]Count Your Blessings: Short Gratitude Intervention Can Increase Academic Motivation
2021.05.13
Keeping a daily gratitude journal for as little as two weeks can help keep students motivated for months
Our dynamically changing lifestyle can make it hard for many to stay motivated on work and study, which calls for new intervention strategies. In a recent study published in BMC Psychology, researchers explore how nurturing feelings of gratitude can enhance motivation among college students. Their results show that a keeping a daily gratitude journal for only two weeks has a positive impact on academic motivations that can last months.
It is difficult for us to succeed in whatever we set out to do if we lack motivation. We usually need it as a driving force to achieve both short- and long-term goals, from household chores to getting a degree. However, because of the ongoing pandemic, our lifestyles have been subjected to drastic and dynamic changes, and many work- and study-related activities are now carried out online exclusively. This, among other complex factors, have made it difficult for some people to stay focused and motivCount Your Blessings: Short Gratitude Intervention Can Increase Academic Motivationated, and psychology researchers are trying to find effective and widely applicable solutions to address such problems.
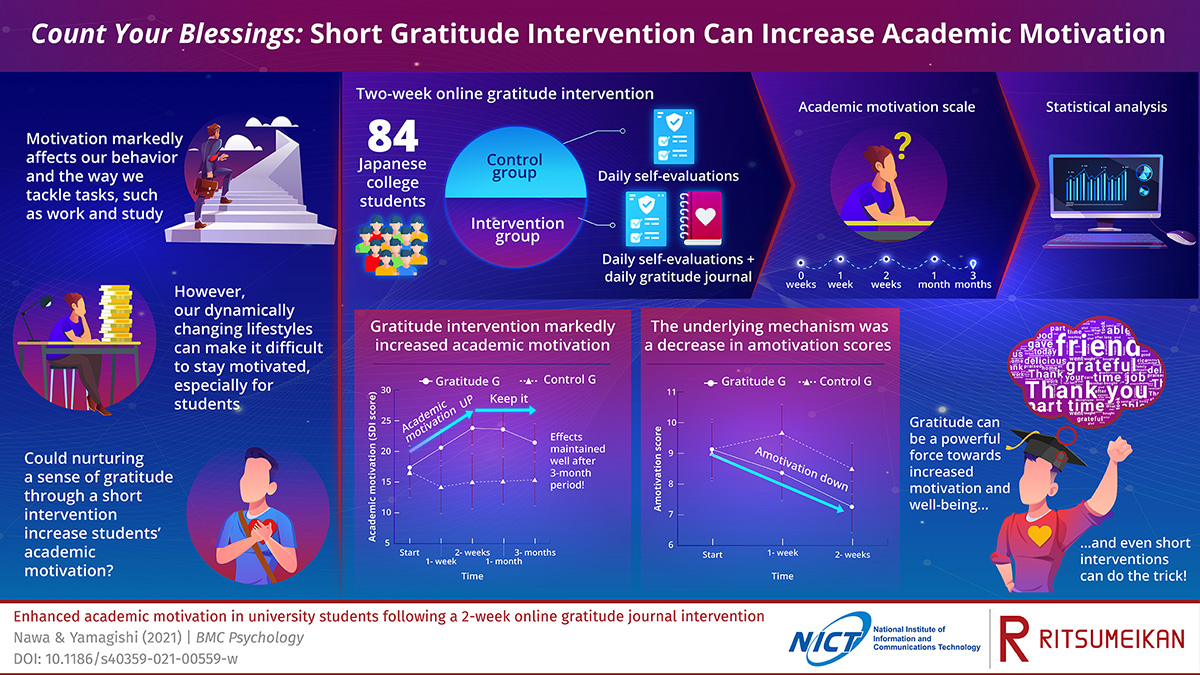
In a recent study published in BMC Psychology researchers from Ritsumeikan University and the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Japan, have explored a simple strategy to increase motivation in college students by nurturing a positive emotion: gratitude. Many studies have shown that even short “gratitude interventions,” which are activities that increase an individual’s awareness of feelings of gratitude, can have a lasting positive effect on that person’s mood, satisfaction, and well-being. However, based on previous studies, the available evidence on the effect of such interventions on academic motivation is somewhat inconclusive. This prompted the researchers to test the effects of a different type of gratitude intervention: daily gratitude journaling.
“Our main hypothesis was that engaging in an online gratitude journal by writing down up to five things one felt grateful for each day could make students be more aware of their academic opportunities—their ‘blessings’—and help them re-evaluate their motives and goals, ultimately improving their motivation,” explains Dr. Norberto Eiji Nawa from NICT, first author of the study. They recruited 84 participants, all Japanese college students, and divided them into a control group and an intervention group. Over the course of two weeks, students in both groups had to evaluate aspects of their daily life through online questionnaires each day, but only the intervention group had to keep the online daily gratitude journal. At the start of the intervention and after 1, and 2 weeks, and 1 and 3 months, the participants had to complete the Academic Motivation Scale (AMS), a tried-and-tested tool for measuring different aspects of academic motivation.
The results were certainly promising; through statistical analyses, the researchers found that the gratitude intervention through daily journaling significantly increased the students’ academic motivation. Most notably, this robust positive effect was not restricted only to the two-week period of the intervention, as the increased level of academic motivation was maintained even after three months. In addition, through an exploratory analysis, the researchers established that the enhancement in academic motivation was mostly driven by a decrease in “amotivation scores.” Amotivation, in this context, refers to the state in which a person perceives that their own actions are irrelevant to the resulting outcomes, leading to feelings of helplessness and incompetence.
Academic motivation can be one of the primary determinants of both academic achievements and satisfaction with school life, and developing widely applicable intervention strategies is critical to foster student growth. “Online interventions have the advantage of being more accessible, scalable and affordable to large portions of the population. Gathering solid evidence to support their deployment will be essential to unleash their true potential in the future,” concludes Professor Noriko Yamagishi from Ritsumeikan University. Fortunately, it appears that the positive impact of gratitude interventions extends well beyond the already-documented effects on individual well-being.
This study was partly supported by a research grant from the Ritsumeikan Inamori Philosophy Research Center. This Center aims to promote multidisciplinary research on the management philosophy advocated by Dr. Kazuo Inamori, a prominent Japanese entrepreneur and renowned philanthropist. With this major goal in mind, Professor Yamagishi, alongside Dr. Nawa, have been working on the scientific elucidation of the emotions of "altruism" and "gratitude" from the perspective of cognitive psychology and neuroscience. This particular study was conducted as part of this more overarching research. Until the day these human emotions become clearer, we can safely give this piece of advice: remember to count your blessings.
Reference
- Title of original paper:
- Enhanced academic motivation in university students following a 2-week online gratitude journal intervention
- Journal:
- BMC Psychology
- DOI:
- 10.1186/s40359-021-00559-w
About Ritsumeikan University, Japan
Established in 1869 with a spirit of liberalism and internationalism, Ritsumeikan University is one of the top-ranking universities in Japan; it was the first to be rated by Quacquarelli Symonds. The university now counts with three main campuses in Kyoto, Shiga and Osaka and boasts over 36,000 students. It is the No. 1 recommended destination for exchange students and even offers the opportunity to earn some degrees entirely in English. Its educational philosophy is based around peace and democracy, and the university strives to face the current era of rapid changes with a rich diversity of people and ideas.
Website: https://en.ritsumei.ac.jp/
About the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Japann
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) is Japan’s sole National Research and Development Agency specializing in the field of information and communications technology and is charged with promoting the ICT sector as well as research and development in ICT, which drives economic growth and creates an affluent, safe and secure society.
Website: https://www.nict.go.jp/en
About Professor Noriko Yamagishi from Ritsumeikan University, Japan
Noriko Yamagishi received a PhD from Purdue University, USA, in 1995 and an MBA with Dean’s honors from McGill University in 2016, Canada. She worked as postdoctoral fellow at UC, San Diego, USA and the University of London, UK, and as senior researcher at the Advanced Telecommunications Research Institutes International and the Center for Information and Neural Networks (CiNet), National Institute of Information and Communications Technology. She joined Ritsumeikan University as a Professor in 2019, where she now leads the Yamagishi Vision Dynamics Laboratory. Her research interests lie in the fields of cognitive psychology, cognitive neuroscience, especially in vision, attention, emotion, and human wellbeing.
About Norberto Eiji Nawa from the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Japan
Norberto Eiji Nawa is a senior researcher and principal investigator at the Center for Information and Neural Networks (CiNet), Advanced ICT Research Institute, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology. He received a PhD in Informatics from Kyoto University, Japan, in 2003. His research interests lie in the fields of psychological sciences and cognitive neuroscience, including the neural mechanisms underlying episodic memory and emotion processes, the study of gratitude and other positive emotions, and how they relate with the psychology and physiology of human wellbeing.
Funding information
This research was partially supported by a project research fund for the Ritsumeikan Inamori Philosophy Research Center. The funding source was not involved in any stage of the research described in this article.
Media contact:
Kazuki Kurajo
Office of Public Relations
Ritsumeikan University
E-mail: kurajo@st.ritsumei.ac.jp
Press Office
Public Relations Department
National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT)
E-mail: publicity@nict.go.jp

